Why is eSIM rollout a big trend?
eSIM technology is a technology used to replace traditional physical SIM cards in the form of an embedded chip that is integrated inside the device. As an integrated SIM card solution, eSIM technology has considerable potential in the smartphone, IoT, mobile operator and consumer markets.
At present, the application of eSIM in smartphones has been basically spread abroad, but due to the high importance of data security in China, it will take some time for the application of eSIM in smartphones to be spread in China. However, with the advent of 5G and the era of smart connection of everything, eSIM, taking smart wearable devices as the starting point, has given full play to its own advantages and quickly found value coordinates in many segments of the Internet of Things (IoT), achieving co-driven interaction together with the development of IoT.
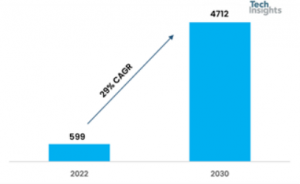
According to TechInsights' latest forecast of the eSIM market stock, global eSIM penetration in IoT devices is expected to exceed 20% by 2023. The global eSIM market stock for IoT applications will grow from 599 million in 2022 to 4,712 million in 2030, representing a CAGR of 29%. According to Juniper Research, the number of eSIM-enabled IoT devices will grow by 780% globally over the next three years.
The core drivers driving the eSIM's arrival in the IoT space include
1. Efficient connectivity: eSIM offers a faster and more reliable connectivity experience than traditional IoT connectivity, providing real-time, seamless communication capabilities for IoT devices.
2. Flexibility and scalability: eSIM technology allows device manufacturers to pre-install SIM cards during the manufacturing process, enabling devices to be shipped with access to operator networks. It also allows users the flexibility to switch operators through remote management capabilities, eliminating the need to replace the physical SIM card.
3. Cost-effectiveness: eSIM eliminates the need for a physical SIM card, simplifying supply chain management and inventory costs, while reducing the risk of lost or damaged SIM cards.
4. Security and privacy protection: As the number of IoT devices increases, security and privacy issues become particularly critical. eSIM technology's encryption features and authorisation mechanism will be an important tool for securing data and providing a higher level of trust for users.
In summary, as a revolutionary innovation, eSIM significantly reduces the cost and complexity of managing physical SIM cards, allowing enterprises deploying large numbers of IoT devices to be less constrained by operator pricing and access schemes in the future, and giving the IoT a high degree of scalability.
Analysis of key eSIM trends
Architecture standards are being refined to simplify IoT connectivity
Continued refinement of the architecture specification enables remote control and configuration of the eSIM through dedicated management modules, thereby eliminating the need for additional user interaction and operator integration.
According to the eSIM specifications published by the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA), two main architectures are currently approved, consumer and M2M, corresponding to the SGP.21 and SGP.22 eSIM architecture specifications and the SGP.31 and SGP.32 eSIM IoT architecture requirements specifications respectively, with the applicable technical specification SGP.32V1.0 currently under further development. The new architecture promises to simplify IoT connectivity and accelerate time-to-market for IoT deployments.
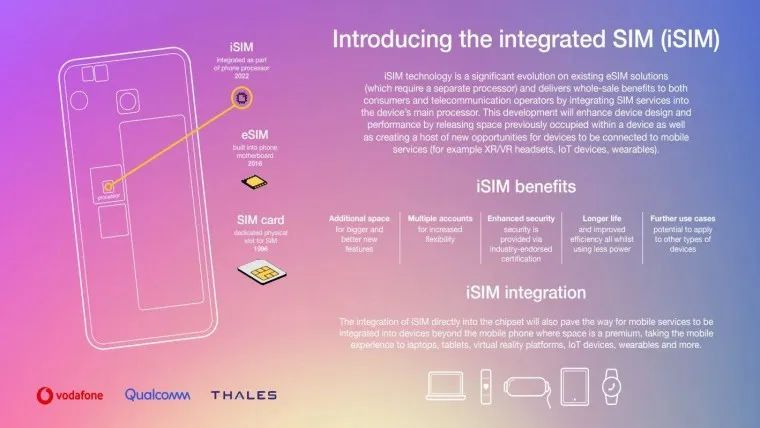
Technology upgrade, iSIM may become a cost reduction tool
eSIM is the same technology as iSIM for identifying subscribed users and devices on mobile networks. iSIM is a technological upgrade on the eSIM card. Whereas the previous eSIM card required a separate chip, the iSIM card no longer requires a separate chip, eliminating the proprietary space allocated to SIM services and embedding it directly into the device's application processor.
As a result, the iSIM reduces its power consumption while reducing space consumption. Compared to a regular SIM card or eSIM, an iSIM card consumes approximately 70% less power.
At present, iSIM development suffers from long development cycles, high technical requirements, and an increased complexity index. Still, once it enters production, its integrated design will reduce component usage and thus be able to save half of the actual manufacturing cost.
Theoretically, iSIM will eventually replace eSIM completely, but this will obviously take a long way to go. In the process, the "plug and play" eSIM will clearly have more time to capture the market in order to keep pace with manufacturers' product updates.
While it is debatable whether iSIM will ever fully replace eSIM, it is inevitable that IoT solution providers will now have more tools at their disposal. This also means that it will become easier, more flexible, and more cost effective to make and configure connected devices.
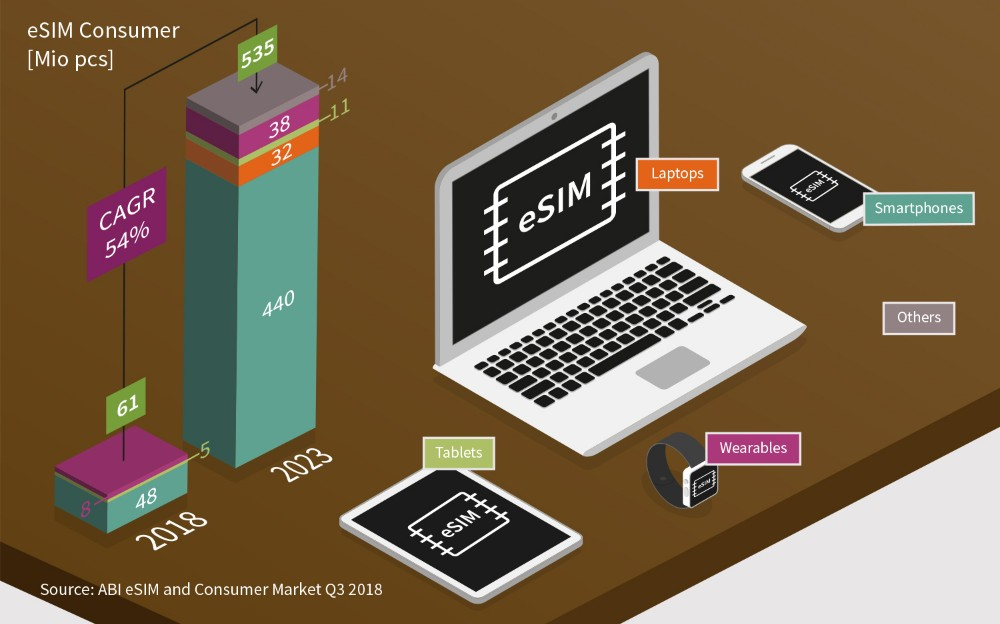
eIM accelerates rollout and solves eSIM landing challenges
eIM is a standardized eSIM configuration tool, i.e. one that allows for the large-scale deployment and management of eSIM-enabled IoT-managed devices.
According to Juniper Research, eSIM applications will be used in only 2% of IoT applications in 2023. However, as the adoption of eIM tools increases, the growth of eSIM IoT connectivity will outpace the consumer sector, including smartphones, over the next three years. By 2026, 6% of the world's eSIMs will be used in the IoT space.
Until eSIM solutions are on a standard track, eSIM common configuration solutions are not suitable for the application needs of the IoT market, which significantly hinders the significant rollout of eSIM in the IoT market. Specifically, subscription-managed secure routing (SMSR), for example, allows only a single user interface to configure and manage the number of devices, whereas eIM enable multiple connections to be deployed simultaneously to reduce costs and thus scale up deployments to suit the needs of deployments in the IoT space.
Based on this, eIM will drive the efficient implementation of eSIM solutions as it is rolled out across the eSIM platform, becoming an important engine to drive eSIM to the IoT front.
Segmentation tapping to unlock growth potential
As the 5G and IoT industries continue to gain momentum, scenario-based applications such as smart logistics, telemedicine, smart industry and smart cities will all turn to eSIM. It can be said that the diversified and fragmented demands in the IoT field provide fertile soil for eSIM.
In the author's view, the development path of eSIM in the IoT field can be developed from two aspects: grasping key areas and holding long-tail demand.
First, based on the reliance on low-power wide-area networks and the demand for large-scale deployment in the IoT industry, eSIM can find such key areas as industrial IoT, smart logistics and oil and gas extraction. According to IHS Markit, the proportion of industrial IoT devices using eSIM globally will reach 28% by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 34%, while according to Juniper Research, logistics and oil and gas extraction will be the industries that benefit most from the rollout of eSIM applications, with these two markets expected to account for 75% of global eSIM applications by 2026. These two markets are expected to account for 75% of global eSIM adoption by 2026.
Secondly, there are ample market segments for eSIM to expand within the industry tracks already in place in the IoT space. Some of the sectors for which data is available are listed below.
01 Smart home devices:
The eSIM can be used to connect smart home devices such as smart lamps, smart appliances, security systems and monitoring devices to enable remote control and interconnection. According to the GSMA, the number of smart home devices using eSIM will exceed 500 million worldwide by the end of 2020
and is expected to increase to approximately 1.5 billion by 2025.
02 Smart Cities:
eSIM can be applied to smart city solutions such as smart traffic management, smart energy management and smart utility monitoring to enhance the sustainability and efficiency of cities. According to a study by Berg Insight, the use of eSIM in smart management of urban utilities will grow by 68% by 2025
03 Smart cars:
According to Counterpoint Research, there will be around 20 million eSIM-equipped smart cars worldwide by the end of 2020, and this is expected to increase to around 370 million by 2025.
Post time: Jun-01-2023